Business Administration (online degree programme)
You want to develop yourself professionally and kick-start your career? Would you like to complete a bachelor's degree but stay in your job?
The online degree programme in Business Administration provides you with a sound basic education in business administration, which you can complete flexibly alongside your job or family. You work on the course content independently on the Moodle learning platform. Weekly live web conferences in the evening as well as recordings of these reinforce the topics. Two to three attendance days per semester provide space for dialogue. If you have studied before, we will check which credits can be recognised.
Facts at a glance
Think globally. Study locally.
The best opportunities for your future. Decide in favour of business studies online at the Suderburg campus!
To the applicationDetails of the degree programme
Fields of activity
Fields of activity
A Bachelor's degree in Business Administration opens up a wide range of career opportunities in industry, commerce, administration and social organisations. You can work in the following areas, for example:
- Personnel management
- Marketing and sales
- Controlling
- Accounting
- Management consultancy
- and many other areas
Programme content
Programme content
On the Business Administration online degree programme, you learn in a practical and flexible way to suit your everyday life. All learning materials for each module are available to you via Moodle. Weekly live web lectures and recordings help you to understand the content. Face-to-face sessions take place at weekends and create space for personal dialogue.
You will learn, for example:
- How to analyse and understand business contexts (e.g. general business administration, economics, business law)
- How accounting, controlling and financing are interlinked
- How to optimise processes and make business decisions
- How to organise projects, personnel or logistics tasks
- How to work with statistics, empirical research and business informatics
- How marketing, e-business and sustainable economic development can complement each other
Over the course of your degree programme, you will have access to electives, a practical project and the Bachelor's thesis, allowing you to set your own individual focus. This will prepare you well for a wide range of business challenges.
Study costs
With us, you only pay the reduced semester fee of currently 234 euros.
In addition, there are the costs for your equipment (laptop/PC, webcam and headset), the use of the internet and travelling expenses for attendance and examination phases.
After the Bachelor
After completing your Bachelor's degree, you can take on new tasks in your current profession and advance your career in a targeted manner. At the same time, you will significantly increase your chances on the labour market. If you want to achieve even more, you can also do a Master's degree programme:
Study programme
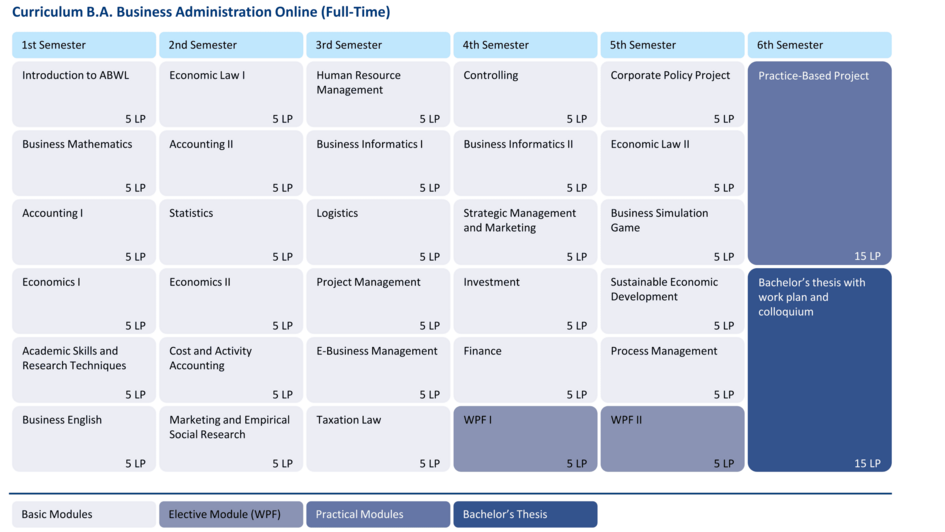
The following study plan shows you a possible structure of how you can spread your online business studies over six semesters. However, you are not bound by fixed timetables: You decide for yourself at what pace you study and when you take which modules - to suit your personal life and work situation.
In terms of content, you can initially expect a solid foundation in business administration, supplemented by practical topics such as project management, business simulations and case studies. Later on, you will deepen your knowledge with elective modules and gain valuable practical experience in the practical project before completing your studies with the Bachelor's thesis.
Study plan
1. Semester Introduction to ABWL (1. Semester) The module teaches the essential aspects of business administration along the operational functions and deals with the following basic topics:
- Business administration as a science
- Subject matter, concepts and fundamentals of business administration
- Companies and corporate management
- Marketing
- Procurement
- Production
- Accounting and controlling
- Investment and financing
- Organisation and personnel
Business Mathematics (1. Semester) - Introduction to logic
- Set theory and numbers
- Equations and inequalities
- Sums and products
- linear systems of equations and linear optimisation
- Relations and functions, properties and graphs
- Sequences and series
- simple interest, annuity and amortisation calculations
- simple differential and integral calculus
- non-linear optimisation
Accounting I (1. Semester) - Company accounting: Definition, areas of company accounting, tasks of internal and external accounting, sub-tasks of bookkeeping, legal sources for bookkeeping, principles of proper bookkeeping, codification of the GoB in the HGB
- Stocktaking, inventory and balance sheet: Definitions of terms according to HGB, dates of inventory, retention period, inventory procedure according to HGB § 241, classification of inventory, assets and capital, balance sheet, legal regulations for balance sheet preparation according to HGB
- Possibilities of balance sheet changes: Asset swaps, nature, meaning, examples, asset/liability increases, nature, meaning, examples, asset/liability decreases, nature, meaning, examples, liability swaps, nature, meaning, examples
- Accounting system: Breakdown of the balance sheet into accounts, From the opening of balance sheet accounts to their closing, Opening and closing balance sheet accounts, The accounting record, Explanation of the term "double-entry bookkeeping"
- Income transactions, determination of material consumption: Determination of income in accounting, determination of material consumption
- Taxable sales, private account: Taxable sales according to EStG, private entries
- Accounting organisation: chart of accounts, chart of accounts, accounting books, document types and document processing
- Postings in the sales and procurement area: purchase and distribution costs, discounts, conversions and reductions, cash discount postings
- Charge postings
- Depreciation and amortisation: Depreciation methods, pro rata temporis depreciation, low-value assets, unscheduled depreciation, acquisition costs, subsequent acquisition costs, sale of used fixed assets
- Annual financial statements: Accruals and deferrals, provisions, valuation of receivables, amortisation of receivables, specific and general bad debt allowances
- Evaluation of accounting: Balance sheet analysis, balance sheet ratios, limits of evaluation
Economics I (1. Semester) - First basic economic ideas
- Household theory
- Business theory
- Elasticity of demand and supply
- The functioning of markets
- Market and state
Academic Skills and Research Techniques (1. Semester) The module focuses in particular on the following topics:
- Self-reflection with regard to academic learning (learning types and learning techniques)
- Reflection on academic aspects, e.g. analytical thinking, forms of academic argumentation, indexing, interpretation and criticism of academic texts, the importance of different forms of publication such as monographs, hand dictionaries, encyclopaedias, specialist journals etc. and the importance of sources and evidence
- Learning and practising study-related techniques (e.g. taking notes, library use, research, excerpting, citing, presenting, discussions on a scientific basis, etc.)
- Thematisation and testing of forms of own text production (written elaboration) and forms of presentation and their quality criteria.
Business English (1. Semester) The content of this module is divided into two areas. Firstly, the specific topics and specialised vocabulary of the business world and secondly, the basic language skills. Each subject area looks at typical business vocabulary, phrases and idioms. Certain subject areas are particularly suitable for practising the grammatical facets of the language. The teaching of the two sections can be combined in this way and the language level is improved from chapter to chapter.
Introduction to ABWL (1. Semester) The module teaches the essential aspects of business administration along the operational functions and deals with the following basic topics:
- Business administration as a science
- Subject matter, concepts and fundamentals of business administration
- Companies and corporate management
- Marketing
- Procurement
- Production
- Accounting and controlling
- Investment and financing
- Organisation and personnel
The module teaches the essential aspects of business administration along the operational functions and deals with the following basic topics:
- Business administration as a science
- Subject matter, concepts and fundamentals of business administration
- Companies and corporate management
- Marketing
- Procurement
- Production
- Accounting and controlling
- Investment and financing
- Organisation and personnel
Business Mathematics (1. Semester) - Introduction to logic
- Set theory and numbers
- Equations and inequalities
- Sums and products
- linear systems of equations and linear optimisation
- Relations and functions, properties and graphs
- Sequences and series
- simple interest, annuity and amortisation calculations
- simple differential and integral calculus
- non-linear optimisation
- Introduction to logic
- Set theory and numbers
- Equations and inequalities
- Sums and products
- linear systems of equations and linear optimisation
- Relations and functions, properties and graphs
- Sequences and series
- simple interest, annuity and amortisation calculations
- simple differential and integral calculus
- non-linear optimisation
Accounting I (1. Semester) - Company accounting: Definition, areas of company accounting, tasks of internal and external accounting, sub-tasks of bookkeeping, legal sources for bookkeeping, principles of proper bookkeeping, codification of the GoB in the HGB
- Stocktaking, inventory and balance sheet: Definitions of terms according to HGB, dates of inventory, retention period, inventory procedure according to HGB § 241, classification of inventory, assets and capital, balance sheet, legal regulations for balance sheet preparation according to HGB
- Possibilities of balance sheet changes: Asset swaps, nature, meaning, examples, asset/liability increases, nature, meaning, examples, asset/liability decreases, nature, meaning, examples, liability swaps, nature, meaning, examples
- Accounting system: Breakdown of the balance sheet into accounts, From the opening of balance sheet accounts to their closing, Opening and closing balance sheet accounts, The accounting record, Explanation of the term "double-entry bookkeeping"
- Income transactions, determination of material consumption: Determination of income in accounting, determination of material consumption
- Taxable sales, private account: Taxable sales according to EStG, private entries
- Accounting organisation: chart of accounts, chart of accounts, accounting books, document types and document processing
- Postings in the sales and procurement area: purchase and distribution costs, discounts, conversions and reductions, cash discount postings
- Charge postings
- Depreciation and amortisation: Depreciation methods, pro rata temporis depreciation, low-value assets, unscheduled depreciation, acquisition costs, subsequent acquisition costs, sale of used fixed assets
- Annual financial statements: Accruals and deferrals, provisions, valuation of receivables, amortisation of receivables, specific and general bad debt allowances
- Evaluation of accounting: Balance sheet analysis, balance sheet ratios, limits of evaluation
- Company accounting: Definition, areas of company accounting, tasks of internal and external accounting, sub-tasks of bookkeeping, legal sources for bookkeeping, principles of proper bookkeeping, codification of the GoB in the HGB
- Stocktaking, inventory and balance sheet: Definitions of terms according to HGB, dates of inventory, retention period, inventory procedure according to HGB § 241, classification of inventory, assets and capital, balance sheet, legal regulations for balance sheet preparation according to HGB
- Possibilities of balance sheet changes: Asset swaps, nature, meaning, examples, asset/liability increases, nature, meaning, examples, asset/liability decreases, nature, meaning, examples, liability swaps, nature, meaning, examples
- Accounting system: Breakdown of the balance sheet into accounts, From the opening of balance sheet accounts to their closing, Opening and closing balance sheet accounts, The accounting record, Explanation of the term "double-entry bookkeeping"
- Income transactions, determination of material consumption: Determination of income in accounting, determination of material consumption
- Taxable sales, private account: Taxable sales according to EStG, private entries
- Accounting organisation: chart of accounts, chart of accounts, accounting books, document types and document processing
- Postings in the sales and procurement area: purchase and distribution costs, discounts, conversions and reductions, cash discount postings
- Charge postings
- Depreciation and amortisation: Depreciation methods, pro rata temporis depreciation, low-value assets, unscheduled depreciation, acquisition costs, subsequent acquisition costs, sale of used fixed assets
- Annual financial statements: Accruals and deferrals, provisions, valuation of receivables, amortisation of receivables, specific and general bad debt allowances
- Evaluation of accounting: Balance sheet analysis, balance sheet ratios, limits of evaluation
Economics I (1. Semester) - First basic economic ideas
- Household theory
- Business theory
- Elasticity of demand and supply
- The functioning of markets
- Market and state
- First basic economic ideas
- Household theory
- Business theory
- Elasticity of demand and supply
- The functioning of markets
- Market and state
Academic Skills and Research Techniques (1. Semester) The module focuses in particular on the following topics:
- Self-reflection with regard to academic learning (learning types and learning techniques)
- Reflection on academic aspects, e.g. analytical thinking, forms of academic argumentation, indexing, interpretation and criticism of academic texts, the importance of different forms of publication such as monographs, hand dictionaries, encyclopaedias, specialist journals etc. and the importance of sources and evidence
- Learning and practising study-related techniques (e.g. taking notes, library use, research, excerpting, citing, presenting, discussions on a scientific basis, etc.)
- Thematisation and testing of forms of own text production (written elaboration) and forms of presentation and their quality criteria.
The module focuses in particular on the following topics:
- Self-reflection with regard to academic learning (learning types and learning techniques)
- Reflection on academic aspects, e.g. analytical thinking, forms of academic argumentation, indexing, interpretation and criticism of academic texts, the importance of different forms of publication such as monographs, hand dictionaries, encyclopaedias, specialist journals etc. and the importance of sources and evidence
- Learning and practising study-related techniques (e.g. taking notes, library use, research, excerpting, citing, presenting, discussions on a scientific basis, etc.)
- Thematisation and testing of forms of own text production (written elaboration) and forms of presentation and their quality criteria.
Business English (1. Semester) The content of this module is divided into two areas. Firstly, the specific topics and specialised vocabulary of the business world and secondly, the basic language skills. Each subject area looks at typical business vocabulary, phrases and idioms. Certain subject areas are particularly suitable for practising the grammatical facets of the language. The teaching of the two sections can be combined in this way and the language level is improved from chapter to chapter.
The content of this module is divided into two areas. Firstly, the specific topics and specialised vocabulary of the business world and secondly, the basic language skills. Each subject area looks at typical business vocabulary, phrases and idioms. Certain subject areas are particularly suitable for practising the grammatical facets of the language. The teaching of the two sections can be combined in this way and the language level is improved from chapter to chapter.
Your advantages with us

+ No tuition fees
+ Bachelor's degree from a state university
+ Time flexibility
+ Live online courses with recording
+ Online learning environment with all learning materials included
+ Intensive support and direct contact
+ Experienced lecturers
+ No NC
Useful links and files
Do you still have questions?
Our Central Student Advisory Service (ZSB) will be happy to support you!
Building Am Exer 45, Room 101 -105
availability by phone:
Monday, Tuesday and Wednesday: 9:00 AM - 3:30 PM
Thursday: 1:00 PM - 3:30 PM
Friday and before holidays: 9:00 AM - 12:00 PM